Most read content
Partner Journal
<Previous issue | Next issue> | Archive
Volume 14 (2); 25 June, 2024
|
|
Research Paper
Investigation of the Engineering Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GRC) Cured with Internal Resistance.
Koc S, Subasi S, Marasli M, Ozdal V.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 14(2): 30-62, 2024; pii:S225204302400004-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.4
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.4
Abstract
In this study, it was aimed to produce glass fiber reinforced concrete (GRC) samples cured with internal resistance by placing resistance wires at different distances within the concrete molds and applying electric current at various voltages, while the mold surfaces were covered with stretch film. The engineering properties of these samples were then investigated. Previous studies have shown that the mechanical properties of conventional concrete, which were subjected to different curing methods, improved compared to samples that did not undergo any curing process. This study aimed to enhance both the engineering properties of the concrete samples and to accelerate the curing process. Glass fiber reinforced concrete (GRC) with dimensions of 50×50×4 cm was produced, and 25, 35, and 45V resistances were applied to three different molds with wire spacing of 5cm, 6cm, and 7cm. With this application, the GRC samples were subjected to internal resistance curing for the first 24 hours. By applying three different voltages to molds with three different wire spacings, 9 concrete samples were produced, along with 1 reference sample that did not contain any resistance wires and was not subjected to any curing process, making a total of 10 different concrete samples. After curing, the concrete samples were cut into 16cm×4cm×4cm GRC mechanical test specimens. The obtained specimens were tested for 7, 14, and 28 day compressive strength, flexural strength, unit weight, and ultrasonic pulse velocity. To examine the microstructure of the GRC samples, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) analyses were conducted. These analyses investigated the physical and chemical development processes of the samples, mass losses, products formed after hydration, and structural behaviors. As a result, it was observed that the early-age strength properties of GRC samples cured with internal resistance showed a partial increase compared to the reference sample that was not internally cured, especially in the 7-day samples. In the 14 and 28-day strength comparisons, it was observed that the cured samples showed improvement in flexural strength. According to the data obtained, the samples subjected to 35 volts of electric current yielded better results, especially in the early ages, compared to the reference sample.
Keywords: Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GRC), Internal Resistance Curing, Microstructure, Engineering Properties
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
|
|
Research Paper
3D Printing in Civil Engineering: Pioneering Affordable Housing Solutions
Firoozi AA and Firoozi AA.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 14(2): 63-75, 2024; pii:S225204302400005-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.5
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.5
Abstract
The escalating global housing crisis necessitates innovative solutions that streamline construction processes while enhancing sustainability and reducing costs. This paper explores the transformative potential of 3D printing technologies in the construction of affordable housing within the field of civil engineering. By examining the technical, economic, and environmental dimensions of 3D printed buildings, the study assesses their scalability for mass housing projects and discusses the significant advantages such as reduced waste, increased precision, and the utilization of recycled materials. The paper also highlights the major challenges to widespread adoption, including regulatory issues, material limitations, and workforce training needs. Through various international case studies, it demonstrates how 3D printing is being successfully implemented to address diverse housing needs and align with Sustainable Development Goals. The study concludes with strategic recommendations for overcoming existing barriers and maximizing the technology’s benefits, outlining a future where 3D printing could fundamentally alter the construction landscape.
Keywords: 3D Printing, Affordable Housing, Civil Engineering, Sustainable Construction, Innovative Technologies, Sustainable Development Goals
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
|
|
Research Paper
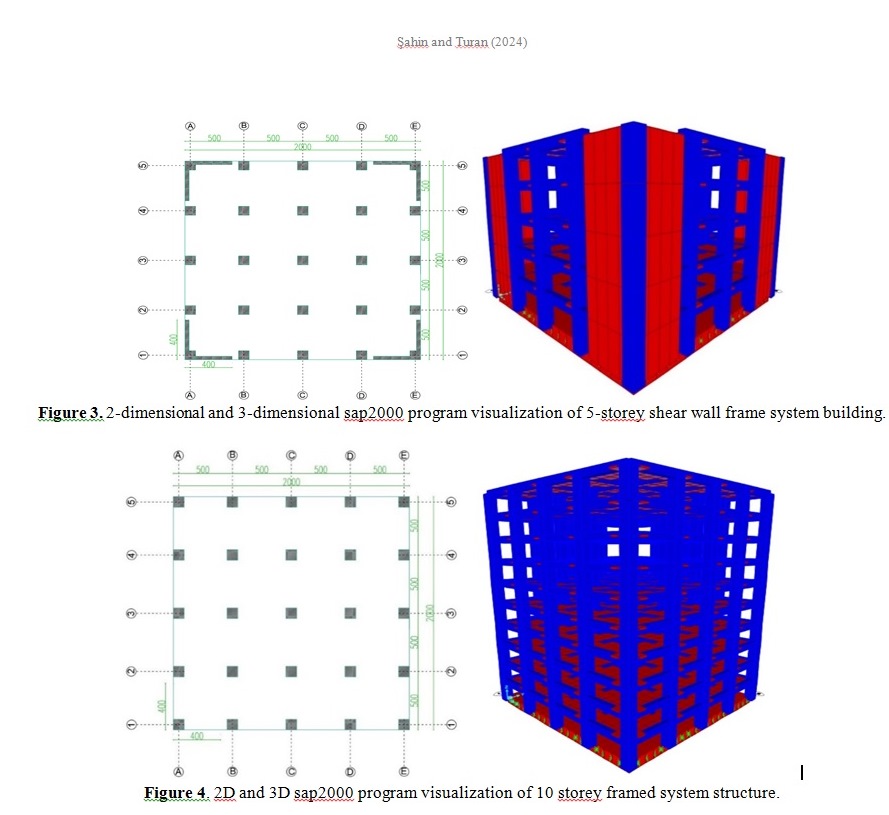
Comparison of 5 and 10 Storey Frame Buildings and 5 and 10 Storey Shear Wall-Frame Buildings Under the Effect of Maras Earthquake According to the Turkish Building Earthquake Code 2018
Şahin F and Turan FC.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 14(2): 76-88, 2024; pii:S225204302400006-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.6
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.6
Abstract
In this study, the differences in the displacements, base shear forces, relative storey drifts and foundation stresses under different earthquake data on different storeys of shear wall frame systems and framed systems are investigated by using SAP2000 program. Within the scope of the study, four buildings with 5-storey frame, 5-storey shear wall frame, 10-storey frame and 10 storey shear wall frame are modelled. All four buildings were designed to be identical with 4 spans in X and Y directions and each span was designed as 5 meters. The height of each floor is designed as 3 meters for all four buildings. In sheared structures, shear walls are designed to be 4 meters from the corner columns to the columns closest to them. The earthquake data to be influenced on all four structures are the earthquake data from the Earthquake Hazard Map of Turkey published by AFAD at the coordinates of 41° latitude, 27° longitude of Kırklareli province, Luleburgaz district. Another earthquake parameter was taken from station 4615 during the earthquake in Kahramanmaras. The data recorded by station 4615 for the 7.6 Mw earthquake in Kahramanmaras was applied to all four structures. These two earthquake data were imposed on these four structures in order to compare the resulting displacements, relative storey drifts, base shear forces and foundation stresses. Since the structures are all symmetrical in both X and Y directions, only one direction of the displacements was calculated. As a result, when both the earthquake data from the Earthquake Hazard Map and the Kahramanmaras earthquake data were applied to these four structures, it was observed that the maximum values of the displacements occurred at the top floors of all structures and the effect of the Kahramanmaras earthquake data was higher in the displacements, relative storey drifts, base shear forces and foundation stresses than the effect of the other earthquake data.
Keywords: Turkish Building Earthquake Code 2018, Kahramanmaras earthquake, storey displacements, relative storey drifts.
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
|
|
Research Paper
Smart Geotechnics: Enhancing Infrastructure Resilience with IoT and AI
Firoozi AA and Firoozi AA.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 14(2): 89-101, 2024; pii:S225204302400007-14
 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.7
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.54203/jceu.2024.7
Abstract
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents transformative opportunities for geotechnical engineering, fundamentally reshaping the monitoring and maintenance of infrastructure. This paper delves into the synergistic application of IoT sensors and AI algorithms to facilitate real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and risk management, significantly enhancing the resilience and sustainability of critical infrastructure such as bridges, tunnels, and foundations. Through a rigorous examination of theoretical frameworks, a review of pertinent literature, and detailed case studies, the study underscores the substantial benefits of these technologies, including improved operational efficiency, enhanced safety, and reduced environmental impact. Additionally, it addresses the predominant challenges of data security, system integration, and scalability, and suggests future research directions and policy considerations to overcome these barriers. The paper advocates for the broader adoption of smart geotechnics, highlighting its crucial role in advancing sustainable and resilient infrastructure in the era of smart cities.
Keywords: Smart Geotechnics, IoT, AI, Infrastructure Monitoring, Predictive Maintenance, Resilient Infrastructure.
[Full text-PDF] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
<Previous issue | Next issue> | Archive
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0)![]()



