Most read content
Partner Journal
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 5 (5); 25 Sep, 2015
 Research Paper
Research Paper
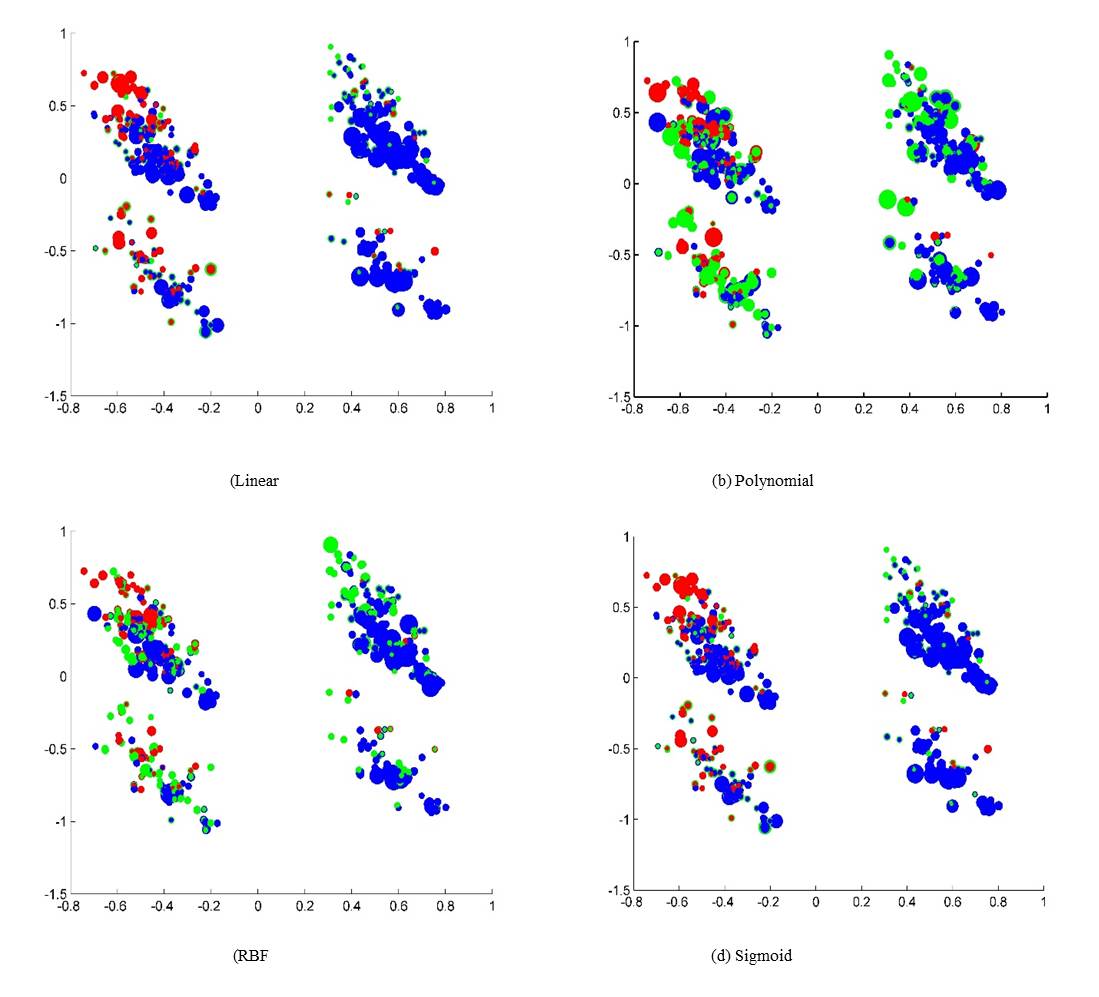
Application of Support Vector Machine for Crash Injury Severity Prediction: A Model Comparison Approach.
Aghayan I., Hadji Hosseinlou M., Metin Kunt M.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 5(5): 193-199, 2015; pii:S225204301500031-5
Abstract
The study presented in this paper investigated the application of using support vector machine with different kernel functions for crash injury severity prediction. A support vector machine model was developed for predicting the injury severity related to individual crashes based on crash data. The models were developed using the input parameters of driver’s age and gender, the use of a seat belt, the type and safety of a vehicle, weather conditions, road surface, speed ratio, crash time, crash type, collision type and traffic flow. Also, three injury levels were considered as output parameters for this study (i.e. no injury, evident injury and fatality). The overall prediction accuracy of the support vector machine model was compared to the multi-layer perceptron, genetic algorithm, combined genetic algorithm and pattern search. The results demonstrated that the constructed multi-layer perceptron’s performance was slightly better than the support vector machine for injury severity prediction. Whereas, support vector machine involves much lower computational cost than multi-layer perceptron because of using a straight forward algorithm in learning phase. The percent of prediction accuracy for the multi-layer perceptron model was 86.2%, which was higher than the support vector machine model with polynomial kernel (81.4%) followed by the combination of the genetic algorithm and pattern search (78.6%) and genetic algorithm (78.1%). The classification results of the two-level (no-injury and evidence injury/fatality) support vector machine found to be 85.3% was higher than multi-class classification (81.4%).
Keywords: Crash Injury Severity Prediction, Genetic Algorithm, Multi-Layer Perceptron, Pattern Search, Support Vector Machine
 Research Paper
Research Paper
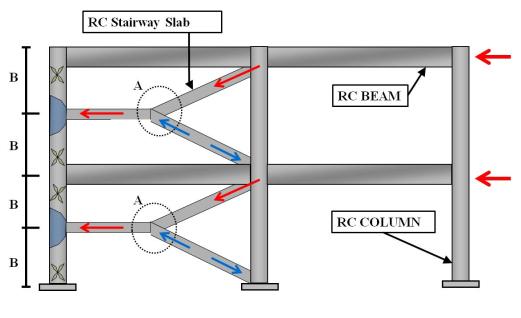
Seismic Structural Failure Potentialities of Newly Constructed Buildings in Iran.
Mohajerani P.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 5(5): 200-209, 2015; pii:S225204301500032-5
Abstract
As Iran is located at high seismic risk region and future ground motions are predicated by seismologist, thus, A Case study was conducted to investigate the major seismic structural failure potentialities due to design and constructional flaws in two province of Iran, Tehran and Esfahan, the former with high seismic risk and the latter with an intermediate risk. More than forty buildings were inspected to find the four major failure potentialities in these two provinces. Two imperfections were found in steel structures and two in reinforced concrete buildings. Design and constructional imperfections in protected zone in steel structures and latticed column details are two main points threaten newly constructed steel structures. In reinforced concrete structures, stairway constructional flaws and wrong pipe passing constructional details are the two main defects covered in this study for this type of structures. This paper also presents solutions for each failure potentiality and recommends some constructional and design hints to increase the safety of structure and make them ready for future seismic excitations.
Key words: Structural failure potentiality, Constructional imperfection, Earthquake, Risk mitigation, Steel structure, Reinforced concrete structures, Iran
 Research Paper
Research Paper
Spatial Analysis of Economic–Social Structure of Urban Worn-Out Textures (Case Study: Mehrabad Region in Bonab City, Iran).
Hashemi R, Karami S, Jeddi M, Rashidi Ebrahim Hesari A.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 5(5): 210-217, 2015; pii:S225204301500033-5
Abstract
Rapid growth of urbanization and the increasing rate of migration has led to urbanization has urban development. Facing new needs in urban life can reduces the tendency of belonging to the city and its cultural heritage. Problems and issues present in the cities and unawareness about values presented in urban structures has led to a rupture between the old and new textures, thereby has caused the problem of worn-out textures. These textures have several social, economic, cultural and physical problems and in needs modernization and restoration. This paper analyzed the physical, social and economic structures on Mehrabad region in Bonab city of Iran which is considered as the main part of Mehrabad neighborhood (one of the two initial cores of the city). Methods used for this work are descriptive-analytic that was done using documentary study, household questionnaires and field study. Demographic, economic, physical and institutional indicators have also been used for data collection. The obtained results showed that in the study area, despite of the presence of low-income residents and lack of improvement and modernization, there is a high rate of public participation and high social capital. Groups of local people the board of Trustees of Mehrabad mosque has also an active role in cooperating and helping residents. Airport people can take active role.
Keywords: Mehrabad Neighbourhood, Socio-Economic Structures of Bonab, Spatial Analysis, Urban Worn-Out Textures
 Research Paper
Research Paper
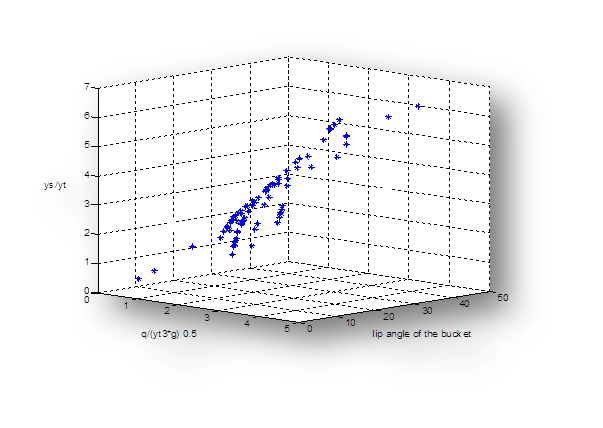
Presenting Relations for Estimate the Scour Depth Due To Free Falling Jets.
Bazargan J and Kalantari M.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 5(5): 218-225, 2015; pii:S225204301500034-5
Abstract
High energy dissipation of the free falling jet from the flip-bucket has been always of utmost significance in prevention of the downstream rivers. Scouring due to falling jet incidence with the river bed will threaten the stability of the dam and related structures, while accumulation of eroded sediments can change tailwater elevation and influence the performance of dam or power plants outlets. So determination of the plunge pool dimensions is an important design consideration. The purpose of this study is to develop empirical exponential relations using the principles of statistics and dimensionless relations by applying dimensional analysis in order to estimate the scour depth due to falling jets considering the effective parameters such as discharge, the difference between water levels in the reservoir and tailwater (jet fall height), tailwater depth, the mean diameter of bed particles and flip-bucket jet angle. By comparing the results of the suggested relations in this study with other investigator results it can be indicated that the developed relations have the maximum correlation coefficient and minimum computational error in an appropriate standard deviation range. Also, the accuracy and dispersion of the 139 collected data series that were used for the proposed relations was higher than the previous studies.
Keywords: Dimensional Analysis, Dimensionless Relation, Flip-Bucket, Maximum Scour Depth, Plunge Pool
Research Paper
Evaluation of Karun River Quality for Irrigation in Khuzestan Province of Iran and Statistical Relationship of TDS and EC in Classified Flow Rates.
Karami O, Hooshmand A, Bazargani S, Lamei M.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 5(5): 226-234, 2015; pii:S225204301500035-5
Abstract
Hydro-Chemical Studies that using regression tests would be efficient operational to save the time and cost, If the regression tests confirm the correctness of regression analysis. In this study, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) and Electrical Conductivity (EC) of Karun River that are varies by flow rates of river, has been separated in three categories, less than 400 Cubic Meters per Second, between 400 and 800 CMS and more than 800 CMS. TDS and EC rate data were analysed using SPSS 18.0 with linear regression model from October 1971 to September 2012. Correctness of estimated values of TDS which estimated with obtained regression equations was evaluated using the t-test, in these way residuals of obtained regression equations should be distributed normally around zero. The values of Sodium Absorption Ratio and Electrical Conductivity of water of Karun River were plotted in the US salinity laboratory diagram for irrigation water in three categories. For classified discharges, respectively about 64.5%, 91.8% and 78.7% of the water samples fall in the field of C3S1, will indicate low sodic waters. The water will cause high salinity hazards with a fairly severe effect on the soil properties, but are suitable for irrigation purpose which requires special careful application.
Keywords: EC, Flow Rate, Hydro-Chemical, Regression, TDS, USSL.
Research Paper
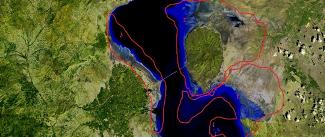
Assessment of Environmental Risks in Marginal Cities of Urumia Lake of Iran Arising from Fluctuations in Its Surrounding Border from 1985 To 2013.
Kiani A, Aghaie V, Badali A, Ghoharmir L, Pasban V.
J. Civil Eng. Urban., 5(5): 235-241, 2015; pii:S225204301500036-5
Abstract
Nowadays, assessment of environmental impacts and potentials is considered as one of the most basic issues in economic, social, urban, and rural planning. Urumia Lake maximum area belongs to May and June and its least development occurs in September and October. Also, its total area is about 500 km. There is an internal flow of water in the west from the north to the south and in the East, it is from South to North, and in the southern coasts it moves in a west- east direction. This factor increases the problems of areas located on the east of the lake that have the maximum regression. Depending on type of its purpose, this study is applying and its nature and methodology are descriptive - analytical. First, the mosaic images of the years 1985 -2013 of Urmia Lake were applied within the software environment, its different parts were cut. Then, using ARC GIS different layers of population, residential areas, elevation, and land use were prepared by overlapping the 5th layer and making a suitable map. These were used to interpret each map. Researches showed that most cities located in the eastern part of the study area such as Tabriz, Azarshahr, Sufian, Miandoab and Marand at most risk and cities like Bonab in which the wind direction is toward the west are at top risk, too, because most regions along the lake are located at elevations below 30 m from the sea level. This factor increases the rate of risk in these areas. If salt displacement by wind and irrigation by farmers lead to salinity of irrigated land and dry-land with an area of about 10,000,000 hectare, these problems will be added over time, and ultimately, will lead to the emigration of hundreds of thousands of people in the area.
Keywords: Environmental Impacts, Ranking, Rating, GIS, Urmia Lake
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive



